Products
-
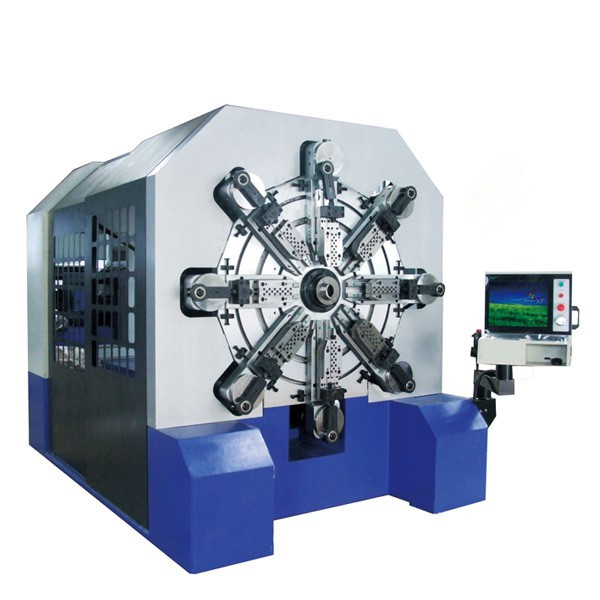
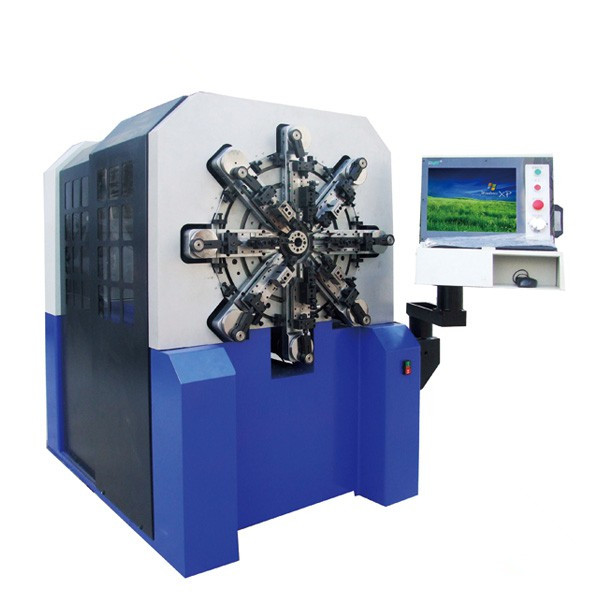
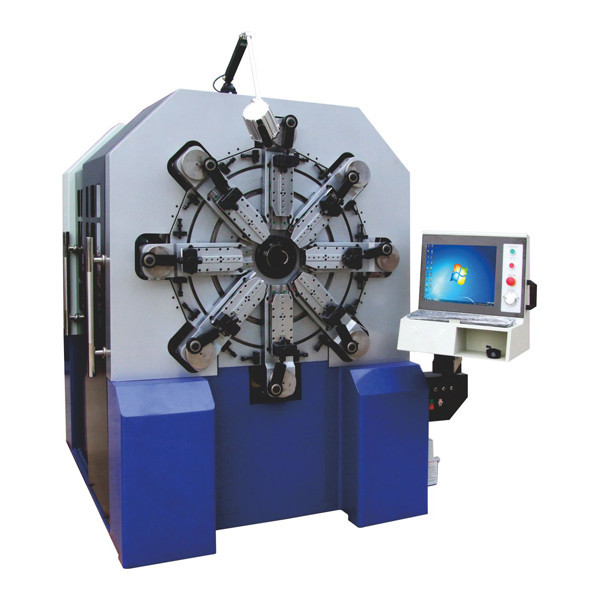
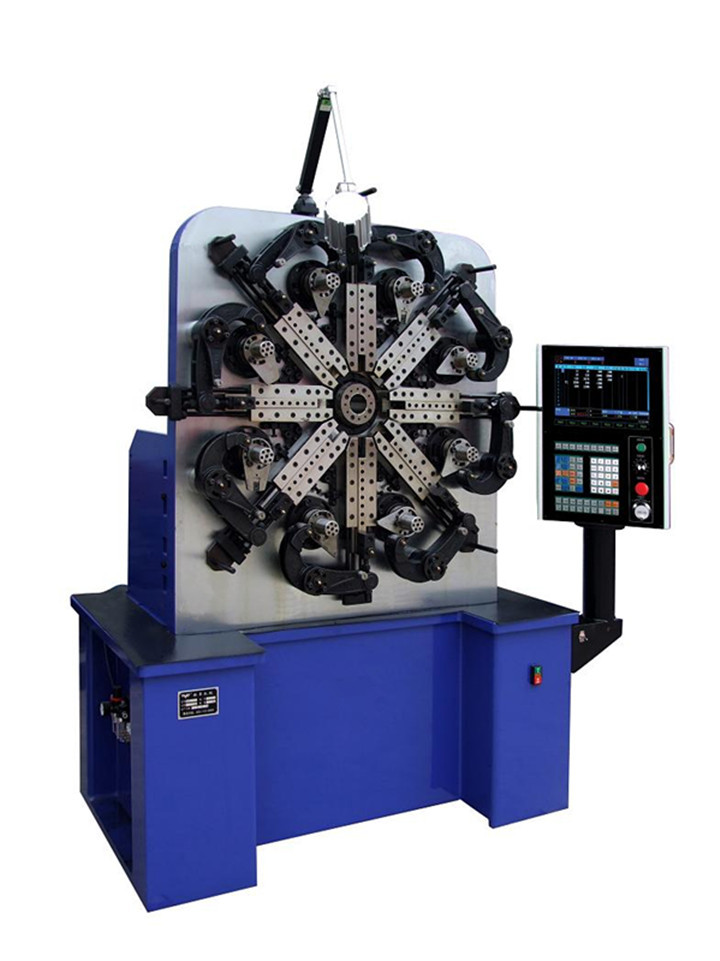
Revolutionary 12 axes spring & wire forming machines that allow spring manufacturers to massively produce a variety of springs with high speed and accuracy!
-
Special camless design equipped with SAMCO’s free arm technolgy that enables our series of spring machines to easily produce all kinds of difficult springs that is 30% or more efficient than traditional cam type spring former.
-
Special camless design equipped with SAMCO’s free arm technolgy that enables our series of spring machines to easily produce all kinds of difficult springs that is 30% or more efficient than traditional cam type spring former.
-
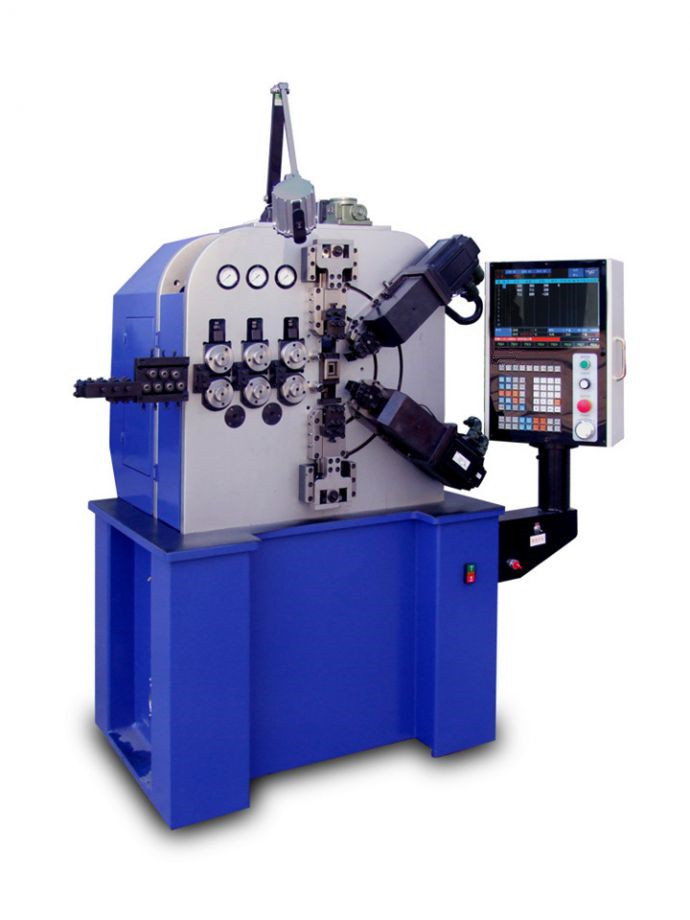
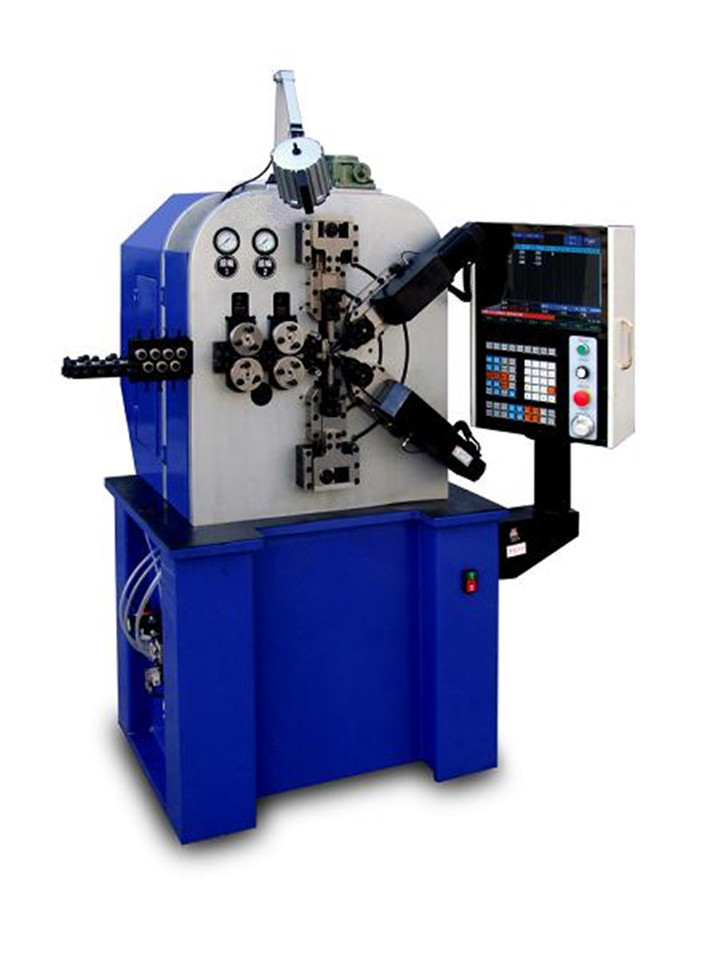
CNC8660 is 6-axis compression spring machine, this CNC spring machine for making compression spring, oil seal spring ,battery spring, torsion machine, etc
-
CNC8635 is six-axis compression spring machine, this CNC spring machine for making compression spring, oil seal spring ,battery spring, torsion machine, etc
-
SAMCO supply spring forming machine, CNC8335 is a 3 axis CNC spring machine, can make compression spring, tension spring, torsion spring, coiling spring and wire forms and etc

About Servomechanism (1)
A servomechanism or servo is an automatic device that uses error-sensing feedback to correct the performance of a mechanism. The term correctly applies only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position or other parameters. For example, an automotive power window control is not a servomechanism, as there is no automatic feedback that controls position -- the operator does this by observation. By contrast the car's cruise control uses closed loop feedback, which classifies it as a servomechanism. A servomechanism is unique among control systems in that it controls a parameter by commanding the time-based derivative of that parameter. For example, a servomechanism controlling position must be capable of changing the velocity of the system because the time-based derivative (rate change) of position is velocity. A hydraulic actuator controlled by a spool valve and a position sensor is a good example because the velocity of the actuator is proportional to the error signal of the position sensor. A servomechanism may or may not use a servomotor. For example, a household furnace controlled by a thermostat is a servomechanism, yet there is no motor being controlled directly by the servomechanism.